Free Reading Speed Test: Average WPM by Age, Education & Language
October 8, 2025 | By Liam Spencer
Ever wondered how your reading speed stacks up against others? Are you curious if your WPM (Words Per Minute) is average, above average, or if there's room for improvement? Understanding your average reading speed is the first step toward enhancing your efficiency. What is the average WPM for an adult? In this comprehensive, data-driven guide, we'll delve into the fascinating world of reading speeds, exploring what constitutes an average reading pace across different age groups, education levels, and even languages, backed by current research and statistics. To get started with a baseline, you can measure your WPM with our free tool.
Decoding Your WPM: What Does Reading Pace Mean?
Before we dive into the numbers, it’s essential to understand what we're actually measuring. Reading speed, typically quantified in Words Per Minute (WPM), is more than just how quickly your eyes can scan a page. True reading efficiency involves a delicate balance between speed and understanding.
Defining Words Per Minute (WPM) and Effective Reading
Words Per Minute is a straightforward calculation: the number of words you read divided by the time it took you in minutes. For example, if you read a 400-word passage in two minutes, your WPM is 200. However, this metric alone is incomplete. Effective reading, the ultimate goal for students and professionals, requires not just speed but also the ability to absorb and retain the information presented.
Beyond Speed: The Crucial Role of Comprehension
Imagine reading a report at 500 WPM but failing to recall any key details afterward. Was that time well spent? This is where comprehension comes in. It’s the measure of how well you understand what you've read. A truly meaningful assessment, like our reading comprehension test, evaluates both speed and understanding to calculate your effective reading speed—the pace at which you can read and still grasp the material accurately.
How We Measure Your Reading Efficiency
Our process is designed to give you a holistic view of your skills. When you take a test on our platform, we first time your reading of a selected passage. Afterward, we present you with a short quiz to assess your comprehension of the text. This dual-metric approach ensures the WPM score you receive is a reliable indicator of your practical reading ability, helping you set realistic goals for improvement.

Average Reading Speed by Age Group & Development
Reading speed is not a static number; it evolves throughout our lives. It develops rapidly during our formative years, adapts to academic and professional demands, and can be maintained with practice into our later years.
Children and Early Learners: Building Foundational Skills
For elementary school students, the focus is on building foundational literacy. By 3rd grade (around 8-9 years old), the average reading speed is typically between 80 and 120 WPM. By 6th grade (11-12 years old), this often increases to 150-180 WPM as they become more fluent and confident readers.
Teenagers & Students: Academic Reading Demands
As students enter high school and college, the volume and complexity of required reading skyrocket. The average reading speed for this group generally falls between 200 and 300 WPM. Those who consistently practice and employ active reading strategies often push toward the higher end of this range to keep up with coursework. It's the perfect time to check your pace and see where you stand against your peers.
Adults: The Average WPM for Professionals & General Readers
For most adults, the average reading speed for non-fiction material settles around 220-250 WPM. Professionals who read extensively for work, such as lawyers or researchers, may develop higher speeds out of necessity. However, many adults find their reading speed plateaus if they don't actively work on improving it.
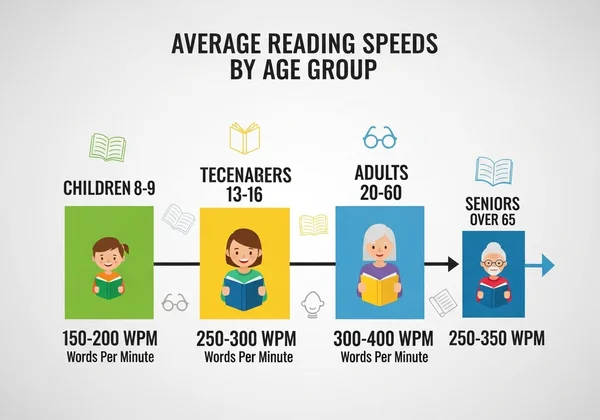
Seniors & Lifelong Learners: Maintaining Cognitive Agility
Reading is a powerful tool for keeping the mind sharp. While there might be a slight natural decline in processing speed with age, active lifelong learners often maintain reading speeds comparable to younger adults. Consistent reading helps preserve cognitive function and ensures that learning never stops.
Education and Its Impact on Your WPM Test Results
Unsurprisingly, your level of education and field of study can significantly influence your reading pace. The more you read complex, specialized texts, the more efficient your brain becomes at processing written information.
From High School to Higher Education: Information Processing
The transition from high school to college marks a significant leap in reading demands. University students are expected to process dense academic journals and textbooks, which trains their minds to read more critically and efficiently. This rigorous practice naturally boosts both speed and comprehension over time, a change you can track when you take a free wpm test.
Specialized Reading in Professional Fields: Text Difficulty
A physicist reading a research paper in their field will likely read much faster and with higher comprehension than a layperson reading the same text. Expertise and familiarity with vocabulary and concepts dramatically reduce the cognitive load, allowing for quicker information processing. Your reading speed is context-dependent and will vary with text difficulty.

The Lifelong Learner's Advantage: Enhanced Visual Span
Individuals committed to lifelong learning constantly challenge their brains with new subjects and vocabulary. This practice broadens their knowledge base and strengthens the cognitive mechanics of reading, such as improving their visual span (the number of words they can see at a glance). This habit is a key driver for maintaining and even increasing reading speed over a lifetime.
Global Perspectives: Reading Speed Across Languages
Does the language you're reading in affect your WPM? Absolutely. The structure, orthography, and character systems of a language play a crucial role in determining average reading speeds. Using our online reading tool can be a great way to gauge your proficiency in a new language.
Alphabetic vs. Logographic Systems
Languages using alphabetic systems (like English, Spanish, and Russian) often have higher WPM averages than those using logographic systems (like Mandarin Chinese and Japanese Kanji). This is because logographic characters contain more information and can be more complex to process visually than individual letters.

Impact of Orthography and Word Length
Languages with a close correspondence between spelling and sound (like Spanish or Italian) are often read faster than those with complex orthography (like English or French). Furthermore, languages with shorter average word lengths may see slightly higher WPM counts.
Multilingualism: A Different Reading Experience
For bilingual or multilingual individuals, reading speed can vary between languages. They typically read fastest in their native or most-practiced language. Testing their speed in different languages is an excellent way for language learners to benchmark their progress and identify areas for improvement.
Factors Beyond Demographics: What Else Affects Your Speed?
Your age, education, and language are not the only factors at play. Several other variables can influence your reading performance on any given day. To see how these factors impact you, you can always test your reading under different conditions.
Text Difficulty & Familiarity
As mentioned earlier, you'll naturally read a familiar, simple text much faster than a dense, technical document filled with jargon. Your purpose dictates your pace; you skim a news article but read a contract slowly and carefully.
Purpose of Reading & Comprehension Goals
Are you reading for pleasure, studying for an exam, or proofreading a document? Your goal sets your speed. Skimming for main ideas will yield a very high WPM, while reading for deep analysis will be much slower.
Physical Environment & Mental State
Your environment matters. A quiet, well-lit room is more conducive to fast reading than a noisy coffee shop. Likewise, your mental state is critical; stress, fatigue, or distractions can significantly slow you down.
Common Reading Habits (e.g., Subvocalization)
Certain habits can limit your reading speed. Subvocalization, the common habit of silently saying each word in your head, is a major bottleneck. It limits your reading speed to your talking speed. Overcoming such habits is a key step toward faster reading.
Benchmark Your Reading Speed & Start Improving Today
Understanding the benchmarks for average reading speed is enlightening, but it's just the starting point. The most important number is your own. Knowing your current WPM and comprehension score gives you a personalized baseline from which you can grow. It empowers you to set achievable goals and track your progress as you learn new techniques to read faster and smarter.
Ready to stop guessing? The journey to becoming a more efficient reader begins now. Take our free, scientifically-designed test and get an accurate assessment of your abilities in minutes. Start improving your reading efficiency today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Reading Speed
What is considered a fast reading speed?
While the average is around 220-250 WPM, a reading speed above 300 WPM is generally considered good or fast for an adult. Highly skilled speed-readers can achieve 500-700 WPM or even higher on familiar material, but this often comes with a trade-off in comprehension. The key is to find your fastest speed while maintaining at least 80% comprehension.
What is the average WPM for an adult?
The average reading speed for an adult reading non-fiction text is approximately 220-250 WPM. This can fluctuate based on the text's difficulty, the reader's familiarity with the subject, and their purpose for reading. For fiction, the pace may be slightly faster.
Does reading on a screen affect your WPM?
Yes, research suggests that people tend to read about 10-30% slower on a screen than on paper. This can be due to factors like screen glare, digital eye strain (Computer Vision Syndrome), and the non-linear reading patterns (like the "F-pattern") that digital layouts encourage. However, with practice and adjustments like proper lighting and font sizes, this gap can be narrowed.
How can I accurately measure my current reading speed?
The most accurate way to measure your reading speed is to use a tool that assesses both your WPM and your comprehension. A simple timer isn't enough because it doesn't verify that you've understood the material. Using a standardized reading speed test will give you a reliable score that reflects your true, effective reading ability. This provides the perfect baseline for tracking your improvement over time. Discover your results today