Improve Reading Memory & WPM: Master What You Read Faster
August 10, 2025 | By Liam Spencer
Have you ever finished reading a page, or even an entire chapter, only to realize you have no idea what you just read? You’re not alone. In our fast-paced world, we often focus on speed, but true learning happens when we retain information. This guide will provide actionable tips to improve reading memory, transforming you from a passive scanner into an active, efficient learner. Let's unlock that potential and make what you read truly stick.
The core challenge isn't just about reading faster; it's about reading smarter. Before diving into these powerful techniques, it's helpful to establish a baseline. You can discover your results on our free platform to see where your current reading speed and comprehension stand. This gives you a starting point to measure your progress as you apply the strategies below.

Why We Forget: Understanding the Retention Challenge
Before we can improve our memory, we must understand why we forget. Forgetting isn't a personal failure; it's a natural brain process. Information overload, passive reading, and a lack of engagement are the primary culprits that prevent new knowledge from moving from our short-term to our long-term memory.
The Science Behind Forgetting: How Memory Works
Our memory operates in stages. First, sensory input is briefly held. If we pay attention, it moves to short-term memory, which has a limited capacity. For knowledge to stick, it must be encoded into long-term memory. This encoding process requires active engagement, context, and repetition. Without these elements, information quickly fades away. Understanding cognitive science can revolutionize how you learn.
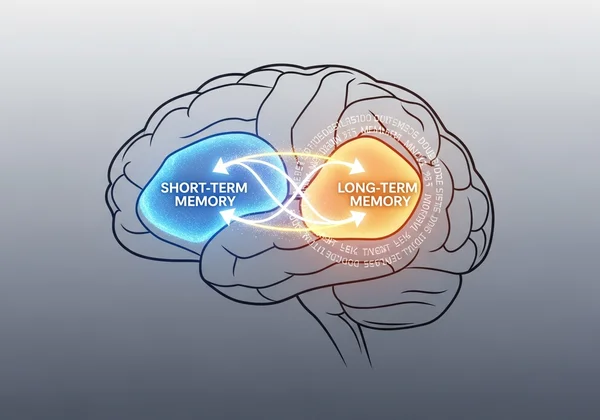
Common Reading Habits That Hinder Memory
Many of us develop habits that sabotage retention without even realizing it. Passive reading, where your eyes simply scan the words without your mind processing them, is a major issue. Other hindrances include reading in distracting environments, failing to review material, and not connecting new information to what you already know. Recognizing these habits is the first step toward building better ones.
Active Reading Strategies: Engaging with the Text
The secret to remembering what you read is to stop being a spectator and start being an active participant. Active reading forces your brain to engage with the material, building stronger neural pathways for memory. These strategies turn reading from a one-way street into a dynamic conversation with the text.
Annotating & Highlighting Effectively for Recall
Highlighting can be a trap if done passively. Instead of coloring entire paragraphs, be selective. Mark only key phrases, powerful concepts, or definitions. Better yet, use the margins for note-taking. Write down questions, summarize concepts in your own words, or draw connections to other ideas. This interaction with the text is a powerful memory aid.

Asking Targeted Questions: The SQ3R Method Demystified
The SQ3R (Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review) method is a classic for a reason—it works. Before reading, survey the chapter to get an overview. Then, turn headings into questions. As you read, actively seek the answers to these questions. This engages your critical thinking and gives your reading a clear purpose, making the information far more memorable.
Summarizing & Paraphrasing: Cementing Your Understanding
After finishing a section or chapter, close the book and try to summarize the main ideas in your own words. This simple act of rephrasing forces your brain to process and condense the information, which is a critical step for long-term retention. If you can't explain it simply, you probably haven't understood it fully.
Memory Techniques for Lasting Knowledge Retention
Beyond active reading, specific memory techniques can dramatically increase your retention rates. These methods are like power-ups for your brain, helping you lock in knowledge for the long haul. Integrating these into your study routine will make a significant difference.
Active Recall & Spaced Repetition: The Power of Testing Yourself
Active recall is the process of retrieving information from memory, like using flashcards or answering questions without looking at the text. This is far more effective than simply rereading notes. Pair this with spaced repetition—reviewing information at increasing intervals—and you leverage one of the most powerful learning principles to combat the forgetting curve.
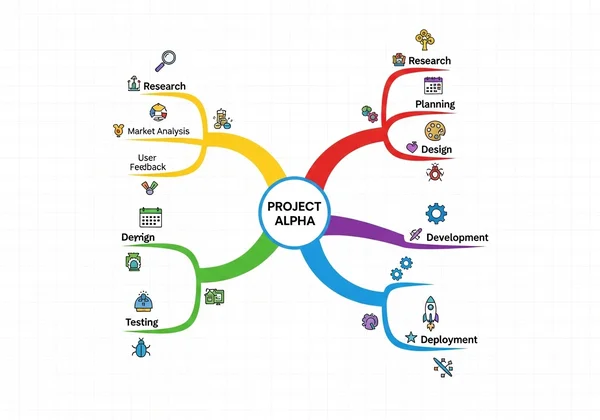
Mind Mapping & Visual Aids: Connecting Ideas Visually
For many, visual learning is key. Instead of linear notes, try creating a mind map. Start with the central topic in the middle and branch out with key concepts, supporting details, and examples. This visual structure helps you see the connections between ideas, creating a mental map that is easier to recall than a wall of text.
Teaching What You Learn: The Ultimate Retention Hack
If you want to truly master a subject, try explaining concepts to someone else. This technique, also known as the Feynman Technique, forces you to simplify complex ideas and identify gaps in your own understanding. The act of teaching solidifies the information in your mind like nothing else.
Building Your Retention Habit: Practice & Assessment
Improving reading memory isn't a one-time fix; it's a skill built through consistent practice and assessment. Just like exercising a muscle, your brain needs a regular workout to get stronger. Creating a structured routine is essential for seeing real, lasting improvement.
Designing Your Daily Reading Practice Routine
Set aside a specific time each day for focused reading. Even 20-30 minutes of applying these active reading and memory techniques is more valuable than hours of passive scanning. A daily routine builds momentum and turns these powerful strategies into second nature.
Utilizing Tools for Tracking Progress and Comprehension
How do you know if your practice is paying off? By measuring it. This is where tools become invaluable. After practicing new techniques, take our wpm test to see how your speed and, more importantly, your comprehension score have improved. Tracking your progress provides motivation and shows you which strategies work best for you.
The Balance: Why Speed and Retention Go Hand-in-Hand
Ultimately, the goal is effective reading—a perfect blend of speed and comprehension. Reading quickly is useless if you don't retain the information. Our platform is designed around this core principle, providing a dual assessment that gives you a complete picture of your reading efficiency. As you practice, you'll find that improved focus and engagement naturally lead to both faster reading and better recall.
Unlock Your Potential: Read Smarter, Remember More
Mastering your reading habits is a pivotal investment in your personal and professional growth. By moving from passive to active reading and using proven memory techniques, you can conquer information overload and truly master what you learn. Stop letting valuable knowledge slip away.
Ready to truly master what you read? Take the vital first step toward smarter reading now. Try our free tool for an instant, accurate measure of your reading speed and comprehension. Begin your journey to becoming an even more effective reader today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Reading Memory & Retention
How can I improve my reading comprehension and memory?
The best approach is to combine active reading strategies with memory techniques. Engage with the text by asking questions and summarizing. Then, reinforce that knowledge using methods like active recall and spaced repetition. Consistency is key.
Does reading speed affect my ability to remember?
It can, but the relationship is complex. Reading too fast can hurt comprehension, while reading too slowly can cause your mind to wander. The goal is to find your optimal pace for efficient learning, where you can maintain both speed and high retention. A reading comprehension test is the best way to find this balance.
How often should I practice reading for better retention?
Daily practice is ideal. Consistency is more important than duration. A focused 20-minute session every day where you apply active reading strategies will yield far better results than a multi-hour cram session once a week.
What's the best way to test my reading comprehension and retention?
The most effective way is to use a tool that measures both speed and understanding. A simple timer only tells half the story. To get a true measure of your effective reading ability, use a comprehensive reading speed test that includes comprehension questions, just like the free one available on our site.